- Microorganisms constitute 70 percent of the biomass on Planet Earth.
- Comparatively few species are adapted to colonize human surfaces and form a complex Meta-Organism with manyfold mutual benefits.
- Occasionally, microorganisms may overcome the barriers of the skin and mucosal surfaces and may multiply locally or in multiple sites inside the body. This process is called infection.
- Infections can be caused by bacteria, viruses, parasites, helminths, and fungi.
- Immediately after infection, numerous defense mechanisms of the immune system are activated to combat replication of the microbes.
- There is a balance between microorganism and human defense mechanisms, which may lead to either asymptomatic infection or result in a wide spectrum of symptoms from mild to severe disease and even death.
- The most important factors in the diagnosis of infectious diseases are a careful history, physical examination and the appropriate collection of body fluids and tissues.
- Laboratory diagnosis requires between 2 and 72 hours.
- Wherever possible, antibiotics should only be used when sufficient evidence of efficacy is available. Then, however, they should be used as early as possible and in high doses.
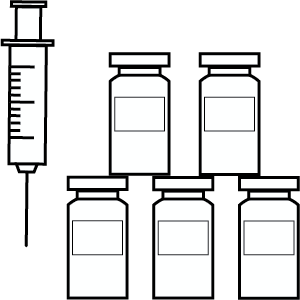
- In addition to everyday hygiene measures, vaccination is the most effective measure to prevent infectious diseases.